Structure
A test case represents one functional check or validation in your system. It defines what to test, how to test, and the expected result.
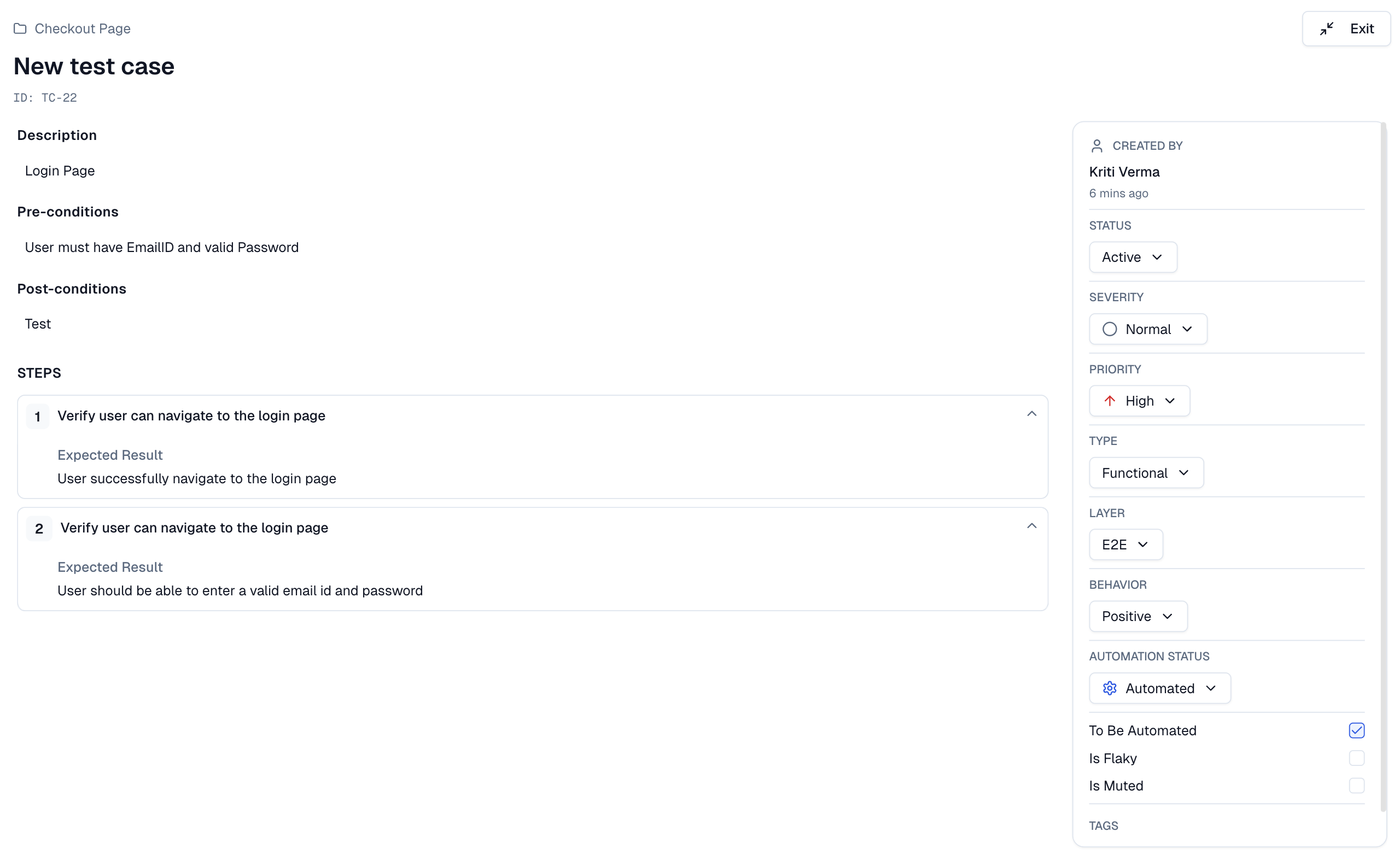
Each test case includes metadata for classification, test steps for execution, and automation flags for tracking readiness.
Each test case is defined by a comprehensive set of fields, visible in the creation form and editing sheet.
1. Core Information
Each test case is defined by a comprehensive set of fields, visible in the creation form and editing sheet.
-
Title: The name of the test case (required).
-
Description: A detailed explanation of what the test case does.
-
Key (ID): A unique, auto-generated identifier (e.g., TC-6297).
2. Classification
-
Status: The current state (Active, Draft, Deprecated).
-
Priority: The urgency of the test (High, Medium, Low, Not Set).
-
Severity: The potential impact of a failure (Blocker, Critical, Major, Normal, Minor, Trivial, Not Set).
-
Type: The category of test (Functional, Smoke, Regression, Integration, E2E, API, Unit, Performance, Security, Accessibility, Other).
-
Behavior: The nature of the test (Positive, Negative, Destructive, Not Set).
-
Layer: The application layer being tested (E2E, API, Unit, Not Set).
3. Automation Fields
-
Automation Status: Whether the test is Manual or Automated.
-
To be automated: Checkbox to flag a manual test for future automation.
-
Is flaky: Checkbox to mark an unreliable or unstable test.
-
Is Muted: Checkbox to silence or skip this test.
4. Pre/Post-conditions
-
Pre-conditions: What must be true before the test runs.
-
Post-conditions: The expected system state after the test finishes.
5. Test Steps (Classic vs. Gherkin/BDD)
-
Test cases can have one or more steps.
-
You can choose between Classic and Gherkin (BDD) formats using tabs.
-
Classic steps include three fields:
-
Action: "What action to perform?".
-
Test Data (optional): "Input data (optional)".
-
Expected Result: "What should happen".
-
-
Click Add Step to add more steps sequentially.
6. Tags and Custom Fields
-
Tags: Add keyword tags (e.g., "Smoke", "regression") for categorization. Tags are comma-separated.
-
Custom Fields: Additional fields can be added, most commonly during a CSV import when a column is "unmapped".
7. Metadata
- Created by: Shows the author's name and a timestamp.