Update project metadata, track monthly execution quota, issue and rotate API keys, connect Integrations, and map branches to environments.
General
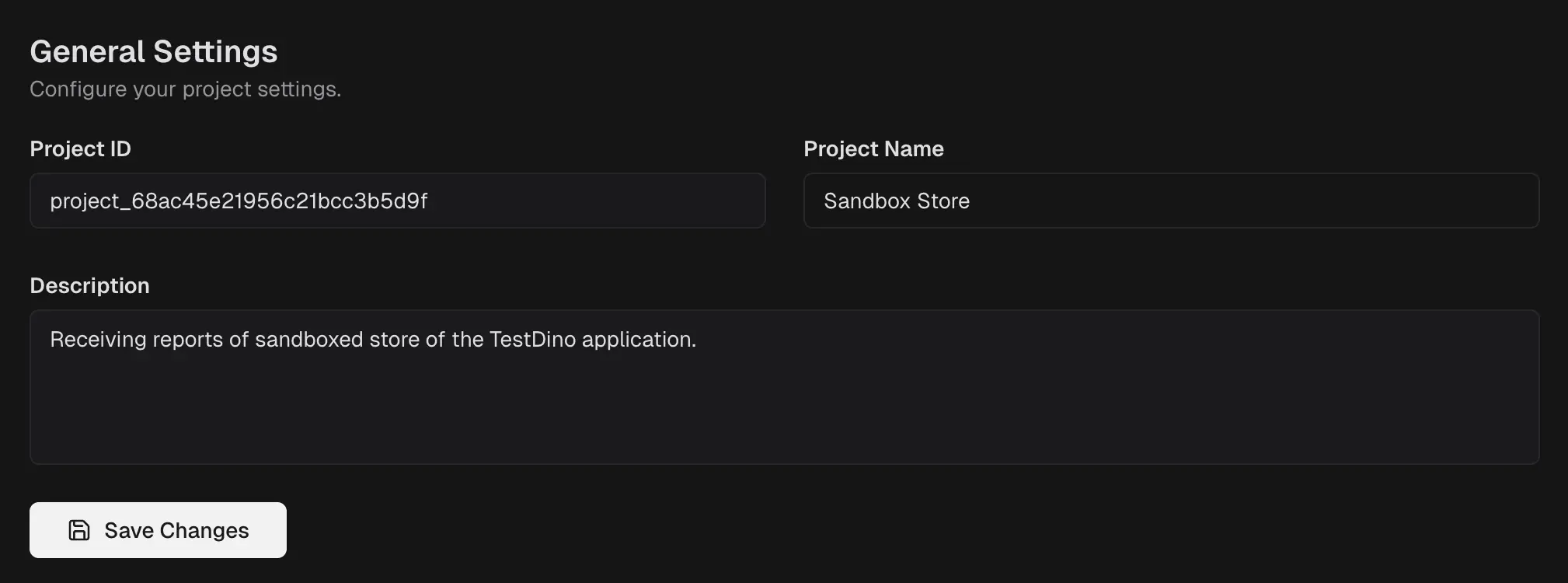 Define the project identity and context shown across the product.
Define the project identity and context shown across the product.
-
Project ID. Read-only identifier used by our platform or support.
-
Project Name. Display name in headers and menus.
-
Description. Short note to describe scope or ownership.
Danger Zone
Permanently delete this project and all of its data. This action cannot be undone. Click Delete Project to proceed.
Before deleting, revoke API keys, disconnect webhooks, and export any required reports.
API Keys
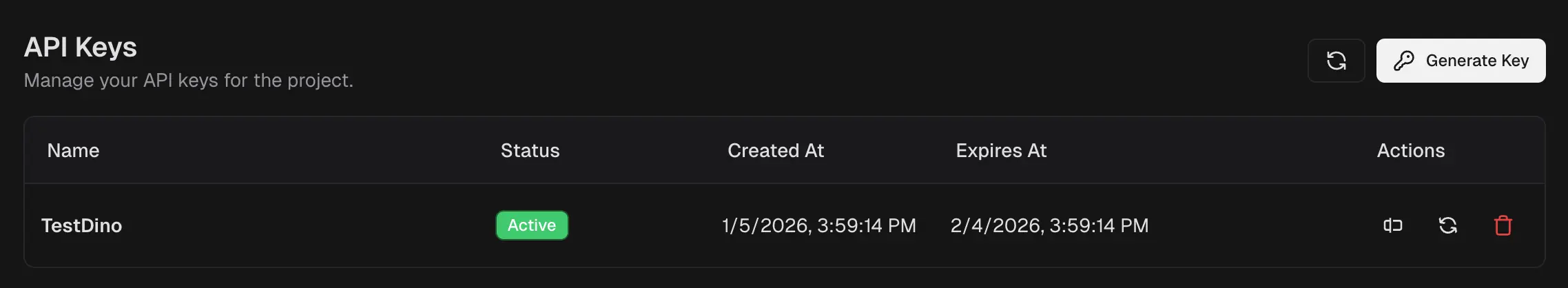 Create and manage credentials for local or CI pipelines and tools that send data to TestDino.
Create and manage credentials for local or CI pipelines and tools that send data to TestDino.
Create a Key
-
Select Generate Key.
-
Enter a Key Name and Expiration (days), 1 to 365.
-
Create the key and store the secret in your secret manager.
Manage Keys
-
Copy or view details. Use row actions to retrieve metadata as allowed.
-
Rotate. Create a replacement key, update CI, then revoke the old key.
-
Revoke or delete. Immediately invalidates the key.
Prefer short expirations for CI. Rotate if exposure is suspected.
Automated Reports
Automated Reports generate PDF summaries of test execution data and send them to specified recipients on a recurring schedule.
Create a Report
- Click Create Automated Report.
- Enter a Report Name.
- Add recipients, configure the schedule, and apply optional filters.
- Select Create.
Use the Enable/Disable toggle to control whether the report generates on schedule.
Recipients
Add one or more email addresses. Each recipient has a type selector for To, CC, or BCC.
Schedule
| Setting | Options |
|---|
| Frequency | Daily, Weekly, or Monthly |
| Time (UTC) | 00:00 to 23:00 (local timezone shown in parentheses) |
| Day of Week | Sunday to Saturday (Weekly frequency only) |
| Report Time Period | Lookback window of 1 to 30 days |
Filters
Filters are optional. Narrow report data by tags or environment.
| Filter | Description |
|---|
| Tags | Add one or more tags to scope the report |
| Environment | Select from branch environment mappings |
Report Actions
| Action | Description |
|---|
| Preview | Download a sample PDF before sending |
| Edit | Update recipients, schedule, filters, and time period |
| Pause/Resume | Temporarily disable or re-enable a report |
| Delete | Remove a report configuration |
AI Features
Control which AI-powered features are active for this project. All AI features are enabled by default for new and existing projects.
Master Toggle
The Enable AI Insights toggle controls all AI features at once. Disable it to turn off every AI feature for the project. Enable it to restore individual feature settings.
Individual Feature Toggles
When the master toggle is enabled, configure each AI feature independently:
| Feature | What it controls |
|---|
| AI Failure Classification | Categorizes failures as Actual Bug, UI Change, Unstable, or Miscellaneous |
| AI Failure Patterns | Detects persistent, emerging, and regression patterns across runs |
| AI Test Case Analysis | Provides root cause analysis, recommendations, and quick fixes per test |
| AI Error Grouping | Groups similar errors by message and stack trace |
Behavior
| Detail | Value |
|---|
| Default state | All features enabled |
| When changes apply | From the next test run |
| Disabled features | Do not generate AI analysis or insights |
| Existing data | Previous AI insights remain visible for past runs |
| Permissions | Admin and Editor roles only |
Disabling an AI feature does not affect other platform functionality. Test execution, reporting, and all non-AI features continue to work normally.
TestDino Add-ons
Status Badges
Embed live SVG badges in GitHub or GitLab READMEs that display test health, flakiness, and test counts from the latest completed run. Configure badges from Integrations → TestDino Add-ons → Status Badges.
For badge types, color scales, and setup steps, see the Status Badges guide.
Integrations
A central place to connect CI/CD, communication, and issue tracking. For installation, permissions, and workflows, see Integrations.
1. CI/CD
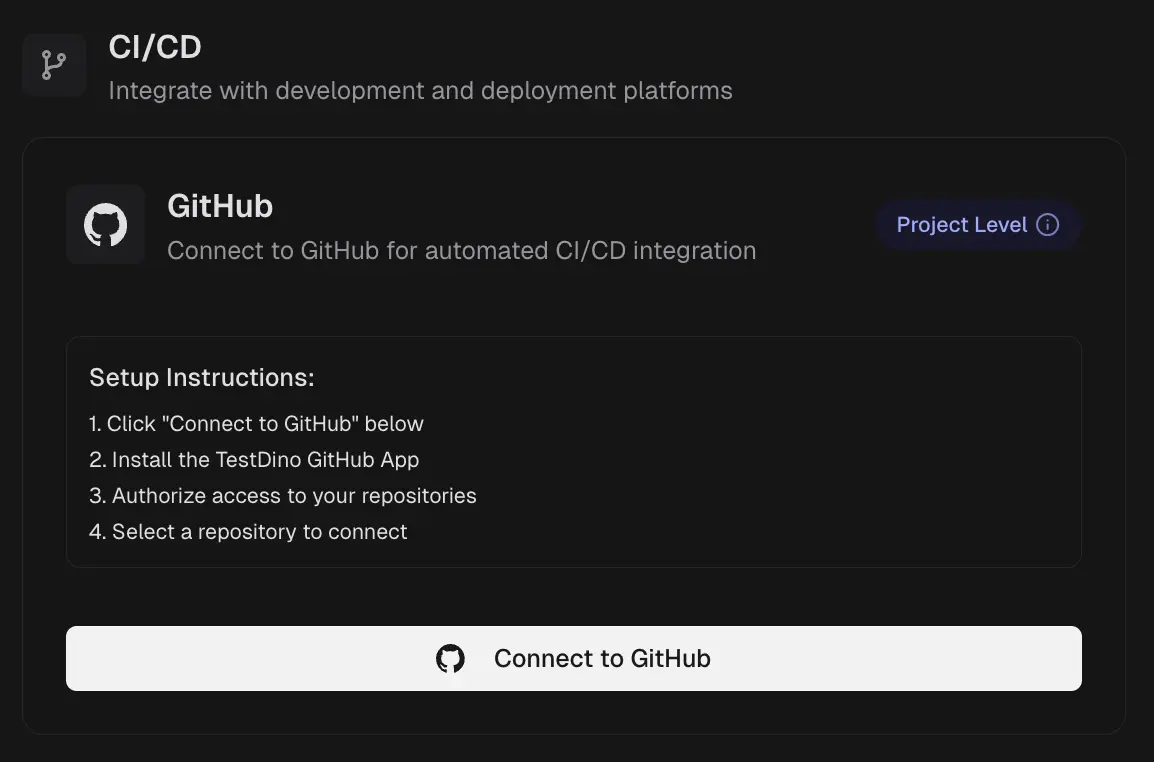 GitHub - Test-run summaries on commits and PRs.
GitLab - Test-run summaries on merge requests and commits. Only one Git provider (GitHub or GitLab) can be active per project.
TeamCity - Upload Playwright test reports from your TeamCity builds directly to TestDino.
GitHub - Test-run summaries on commits and PRs.
GitLab - Test-run summaries on merge requests and commits. Only one Git provider (GitHub or GitLab) can be active per project.
TeamCity - Upload Playwright test reports from your TeamCity builds directly to TestDino.
2. Issue Tracking
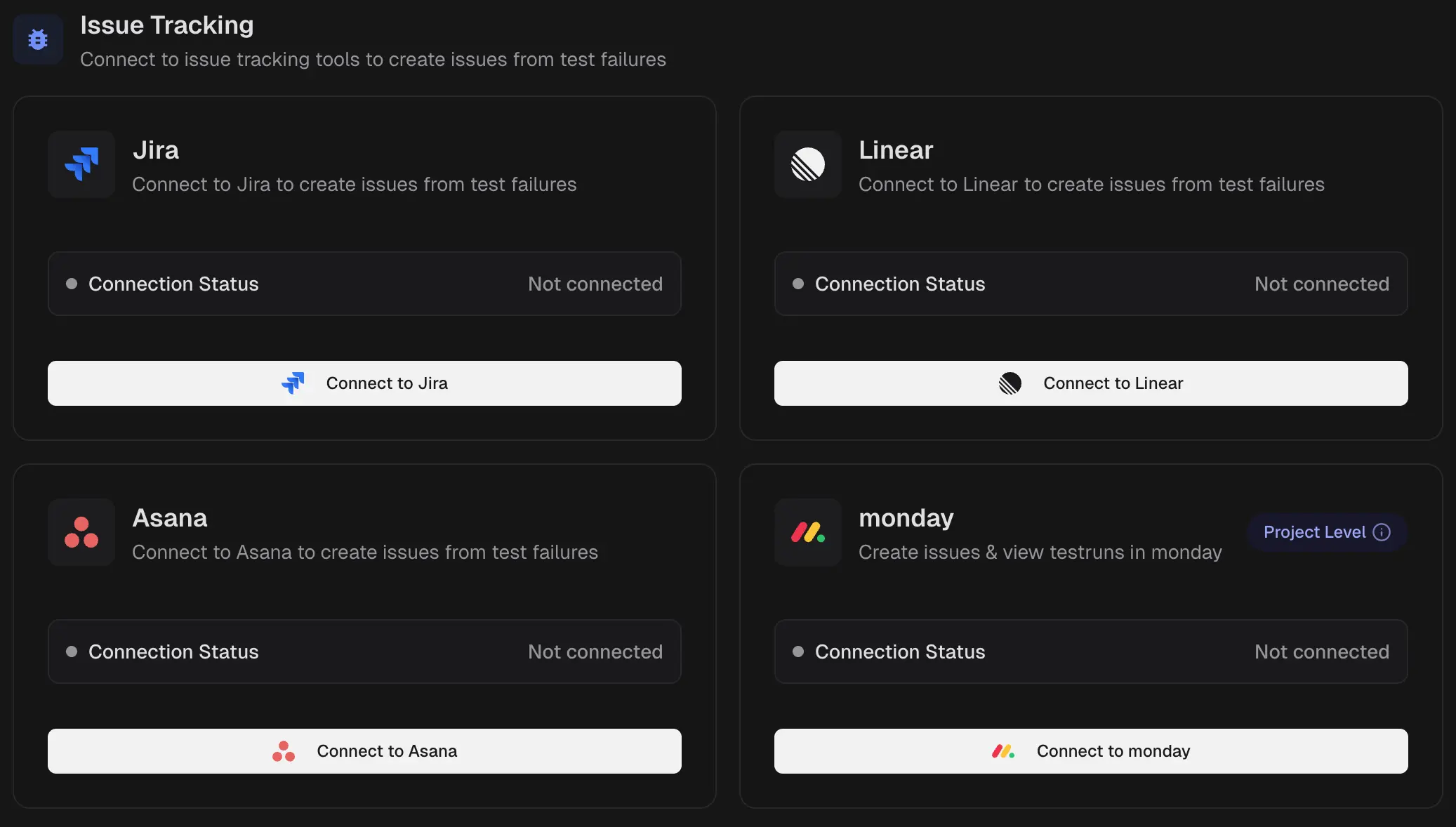 To create issues from failed or flaky tests, use:
To create issues from failed or flaky tests, use:
3. Communication
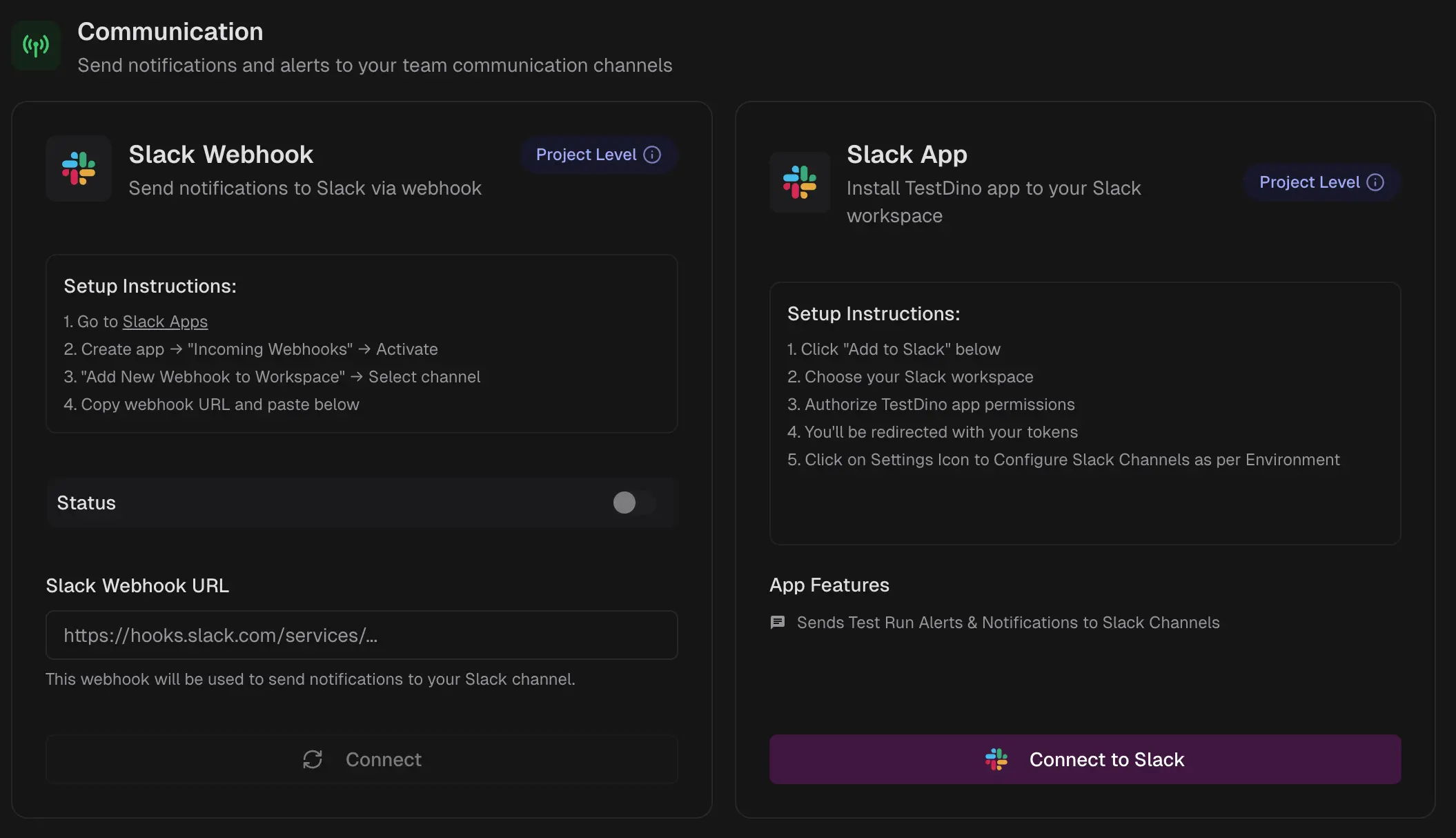
-
Slack Webhook - posts a test run summary to the Slack channel.
-
Slack App - posts a test run summary to the Slack channel mapped to the run’s branch environment.
If no environment mapping matches, TestDino posts the summary to the default Slack channel.Remember: Map each branch pattern to an environment and select a Slack channel for that environment; environment mapping takes precedence over the default channel. This applies to GitHub as well.
Typical Actions
-
Connect the integration using OAuth, then grant the required scopes.
-
Configure targets, such as the default project, team, or channel, and map by environment or branch where supported.
-
For GitHub: Enable bot comments on pull requests and commits, and choose the branches or environments that should receive summaries.
-
For Slack App: Set a default channel, map environments or branch patterns to channels, refresh the channel list, and send a test message.
Branch Mapping
It maps repository branches to specific environments (production, staging, etc.) using exact names or patterns, ensuring your results display in the correct environment throughout the platform.
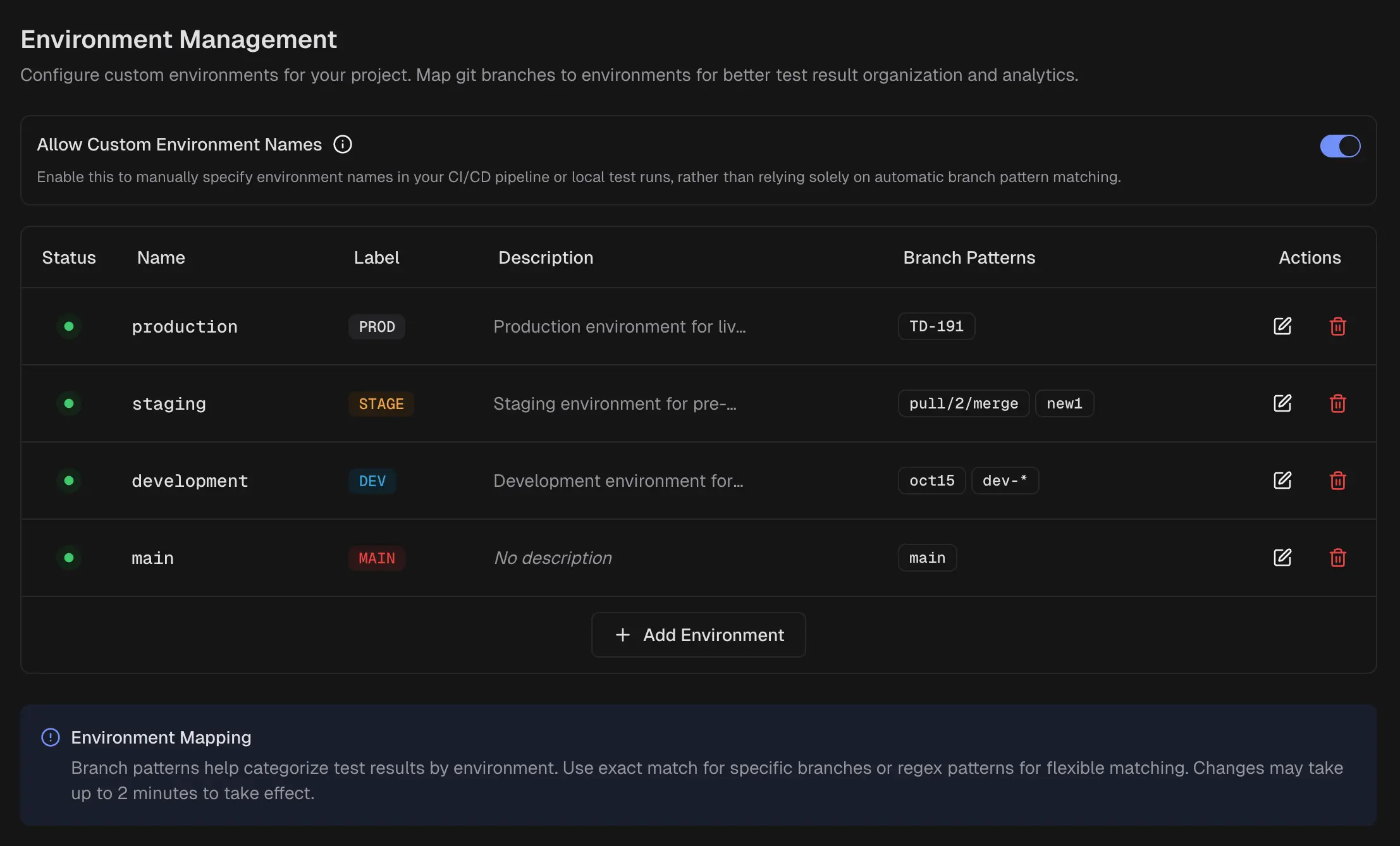
Why does it matter?
End-to-end tests often run on pull requests and short-lived branches. Without mapping, those runs fragment across dozens of branch names.
Mapping rolls them up to the right environment, so pass rates, volumes, and alerts reflect reality.
Add or edit an environment
-
Enter Name and a short Label used in chips and filters.
-
Optionally set a Description and color.
-
Define Branch patterns:
-
Exact match to bind a single branch, for example,
main.
-
Pattern match to bind many branches, for example,
feature/*, release/*, hotfix/*.
-
Save. Changes can take up to 2 minutes to apply.
Note:
-
Environments and branches: A development or staging environment typically encompasses multiple branches, for example,
feature/123 or user/td-123. Production typically maps to one protected branch, such as, main or master. Teams that run tests on PRs opened or merged will execute on the PR’s head branch. Mapping ensures those runs are attributed to the correct environment.
-
Keep labels short, for example, PROD, STAGE, DEV.
-
Review patterns when you add long-lived branches.
-
Limit: up to 10 environments per project.
CLI Environment Override
You can bypass branch mapping and assign test runs to a specific environment directly from the CLI.
1. How it works
When enabled, the --environment flag in your upload command takes priority over branch mapping rules. If you specify --environment=staging, that run goes to staging regardless of which branch triggered it.
This is useful when:
-
You run tests against multiple environments (prod, stage) from a single commit
-
Your CI pipeline targets specific environments that don’t match your branch naming
-
You need manual control over the environment assignment for certain runs
2. Enable CLI Environment Override
-
Go to Project Settings → Environment Settings
-
Turn on CLI Environment Override
-
Click Save to apply the changes.
With the toggle off (default), the CLI flag is ignored, and branch mapping rules apply.
3. Using the flag
Add --environment to your upload command:
npx tdpw upload ./playwright-report --token="your-token" --environment="staging"
Warning:
-
Maximum 10 environments per project. If you’ve hit the limit, the CLI run still succeeds but uses branch mapping instead. You’ll see a warning in the CLI output.
-
Environment names must be valid. Invalid characters cause the upload to fail.
How CLI runs interact with branch mapping updates
-
CLI-created runs: When you update branch mapping rules, test runs created via the
--environment flag keep their original environment. The CLI value is preserved.
-
Branch-mapped runs: Existing runs created through branch mapping update to reflect the new rules.
 Define the project identity and context shown across the product.
Define the project identity and context shown across the product.
 Create and manage credentials for local or CI pipelines and tools that send data to TestDino.
Create and manage credentials for local or CI pipelines and tools that send data to TestDino.
 GitHub - Test-run summaries on commits and PRs.
GitLab - Test-run summaries on merge requests and commits. Only one Git provider (GitHub or GitLab) can be active per project.
TeamCity - Upload Playwright test reports from your TeamCity builds directly to TestDino.
GitHub - Test-run summaries on commits and PRs.
GitLab - Test-run summaries on merge requests and commits. Only one Git provider (GitHub or GitLab) can be active per project.
TeamCity - Upload Playwright test reports from your TeamCity builds directly to TestDino.

