Only runs from the active branch appear. Test runs from other branches are excluded.
What You See
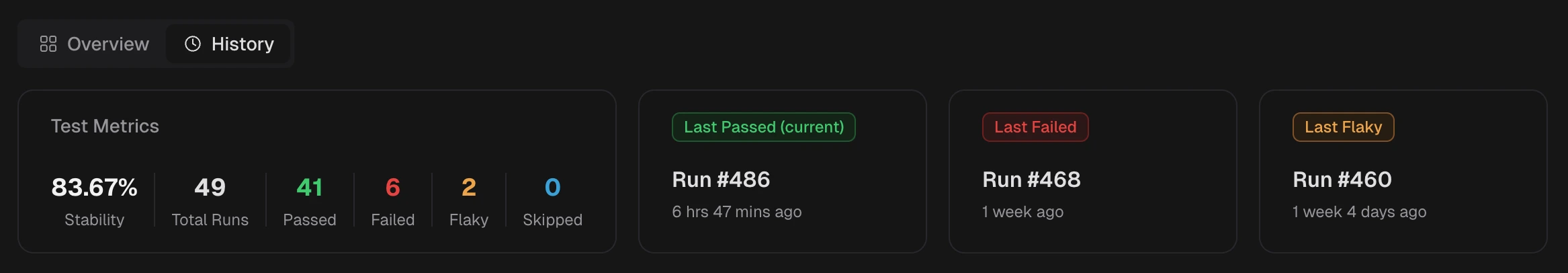
1. Test Metrics
Key metrics for this test on the active branch:-
Stability: Percentage of runs that pass. A 100% stability score means the test passed in all tracked executions.
Stability is calculated as
(Passed Runs ÷ Total Runs) × 100 - Total Runs: The total number of executions tracked on this branch. Provides context for all other metrics.
- Passed / Failed / Flaky / Skipped: Counts for each outcome.
2. Last Status Tiles
Links to the most recent run for each outcome: Last Passed, Last Failed, Last Flaky. Each tile shows the Run # and timestamp. The current label appears when the tile matches the run you are viewing.3. Execution History Table
Lists every execution on this branch in time order.| Column | Description | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Executed at | Timestamp when the test ran | Correlates failures with commits or deployments |
| Run | Unique identifier for the test run | Navigate to the exact run |
| Status | Outcome: Passed, Failed, Flaky, Skipped | Spot trends and recurring issues |
| Duration | Total runtime of the execution | Identify performance regressions |
| Retries | Number of retry attempts | Surfaces flaky or unstable tests |
| Run location | Link to the CI job | Access to the original build and logs |
| Actions | Link to execution details | Inspect evidence and artifacts |
Rows expand to show Error Details for failures or Console Logs if they were captured during execution.
How to Read Stability
Stability measures a test’s reliability on the current branch. The percentage reflects the entire history, not just the most recent run.- 100% Stability: Test passes in every tracked run on this branch.
- < 100% Stability: At least one run failed or was flaky, even if the latest run passed.
Why It Matters
- Confirm whether a failure is a regression or a recurring issue.
- Track retry frequency as a stability signal.
- Spot duration changes that indicate performance drift.
- Use run links to inspect evidence and CI context.