Quick Reference
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Core fields | Title, description, key |
| Classification | Status, priority, severity, type, behavior, layer |
| Automation fields | Manual/Automated, flaky, muted |
| Test steps | Classic (Action/Data/Expected) or Gherkin (Given/When/Then) |
| Custom fields | Text, textarea, number, dropdown, checkbox |
| Attachments | Screenshots, documents, test data files |
| Version history | Change tracking, comparison, restore |
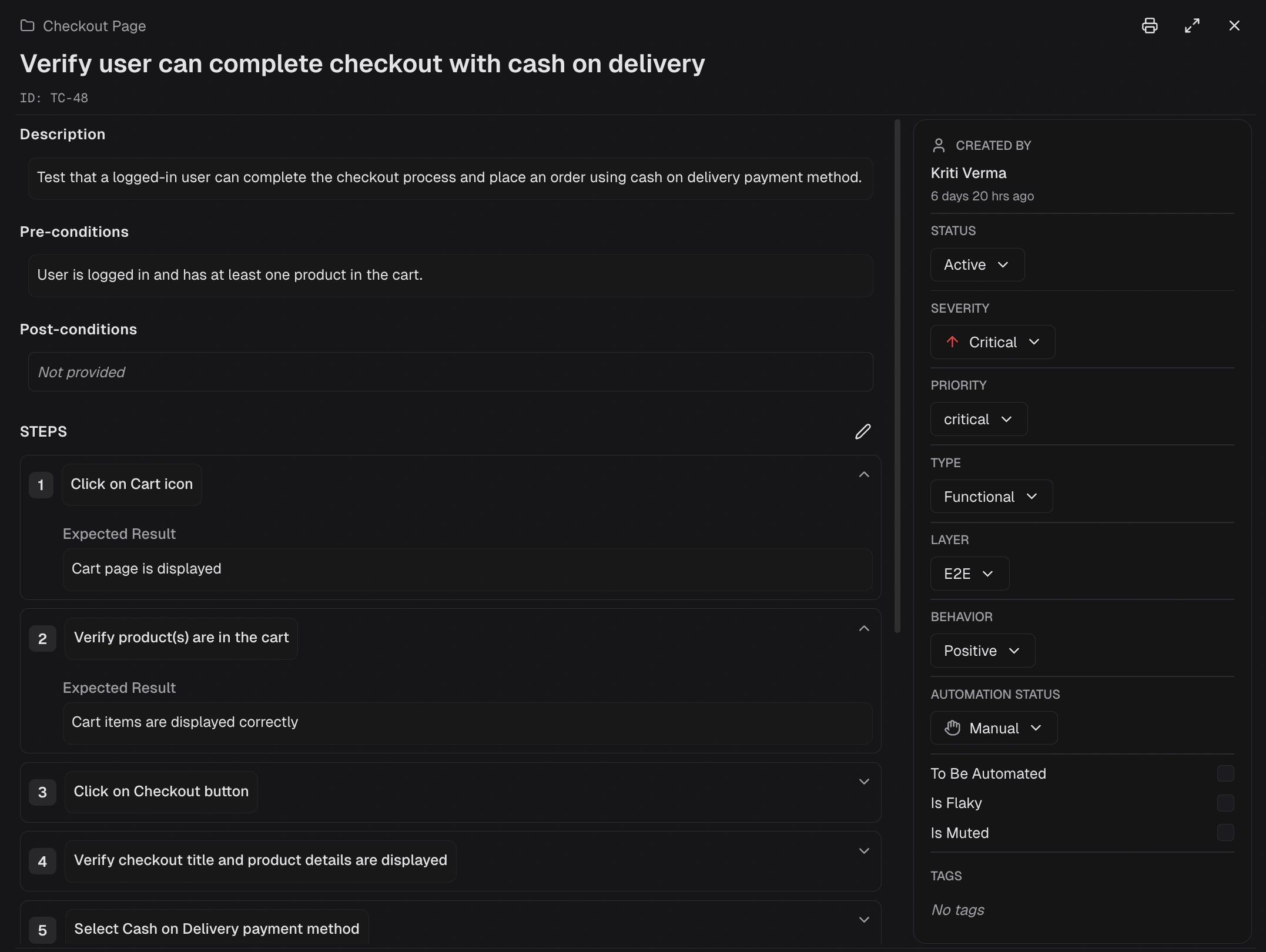
Core Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Text (required) | The name of the test case |
| Description | Text | A detailed explanation of what the test case validates |
| Key (ID) | Auto-generated | A unique identifier (e.g., TC-6297) |
Classification
| Field | Options |
|---|---|
| Status | Active, Draft, Deprecated |
| Priority | Critical, High, Medium, Low, Not Set |
| Severity | Blocker, Critical, Major, Normal, Minor, Trivial, Not Set |
| Type | Functional, Smoke, Regression, Integration, E2E, API, Unit, Performance, Security, Accessibility, Other |
| Behavior | Positive, Negative, Destructive, Not Set |
| Layer | E2E, API, Unit, Not Set |
Automation Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Status | Dropdown | Manual, Automated, To Be Automated |
| Is Flaky | Checkbox | Mark an unreliable or unstable test |
| Is Muted | Checkbox | Silence or skip this test |
Pre/Post-conditions
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Preconditions | What must be true before the test runs |
| Postconditions | The expected system state after the test finishes |
Test Steps
Test cases support one or more steps. Switch between Classic and Gherkin (BDD) formats using tabs in the step editor.- Classic
- Gherkin (BDD)
Classic steps use three fields per step:
Click Add Step to append additional steps.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Action | What action to perform |
| Test Data | Input data (optional) |
| Expected Result | What should happen |
Tags
Add keyword tags (e.g.,smoke, regression, login) for cross-suite categorization. Tags are comma-separated and can be applied during creation, editing, or bulk operations.
Custom Fields
Create project-specific fields beyond the built-in set. Custom fields appear alongside standard fields in the creation form and editing sheet.| Type | Use for | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Short information | Environment: “Staging”, Build: “v2.1.5” |
| Textarea | Long notes | Special instructions, test data details |
| Number | Numeric data | Execution time: 5 (minutes) |
| Dropdown | Pick one option | Browser: Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge |
| Checkbox | Yes/No toggle | Requires VPN: Yes / No |
Custom Field Limits
| Limit | Value |
|---|---|
| Dropdown options | 50 per field |
| Text field length | 500 characters |
| Textarea field length | 5,000 characters |
Manage custom fields in Project Settings. Unmapped columns during CSV import are automatically created as custom fields.
Attachments
Attach screenshots, documents, or test data files to any test case. Attachments provide additional context for manual test execution or review.| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Max attachments per test case | 5 files |
| Supported actions | Upload, view, download |
Attachments can be enabled or disabled at the project level in Project Settings.
Version History
Track all changes made to a test case over time. Version history records who changed what and when, providing a full audit trail.| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Change log | View a chronological list of all edits |
| Diff view | Compare any two versions side by side |
| Restore | Revert a test case to a previous version |
Version history can be enabled or disabled at the project level in Project Settings.
Metadata
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Created by | Author name and timestamp |